A condensation reaction is a type of a reaction where two molecules combine to form a single molecule, often water, is then removed from the reaction. For example, when two amino acid molecules combine in a condensation reaction, a covalent bond forms between the amine nitrogen of the first amino acid and the carboxyl carbon of the second amino acid. This results in a molecule of water being removed as a product. This is illustrated below:
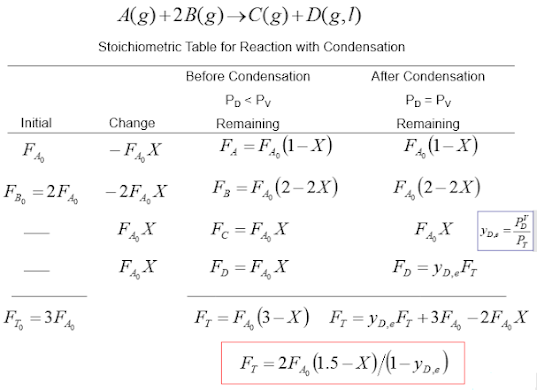
Now lets consider a condensation reaction between two gaseous reactants A and B resulting in products C and D. The stoichiometric table can help us get a general expression for flow rate as a function of mole fraction and conversion as shown:









No comments:
Post a Comment