Entropy is an extensive property, like mass and energy, that can be used to characterize the state of thermodynamic systems at equilibrium. The entropy of a system changes as a result of a process but it is not a conserved quantity. Generation of entropy, Sgen, is equal to the entropy change of the universe, i.e.,
Sgen = ΔSuniverse
=ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings ≥ 0 (1)
ΔSsystem may be less than zero. However, ΔSuniverse
is either zero (reversible process) or greater than zero (irreversible
process).
For an open system (both mass and energy is exchanged
with surroundings), the rate of entropy generation is expressed as:
Ṡgen = Ṡsystem + Ṡsurrounding (2)
The
rate of entropy change of the system is expressed as:
The
entropy of the surroundings may change through two ways: (i) mass flow, (ii)
heat transfer. Note that entropy transfer has nothing to do with work. Thus,
This
is also known as the entropy balance. Note that dQsurr = − dQsys
and dSgen ≥ 0.
Simplifying
Eq. 6 for different types of systems is given below:
Isolated Systems
Since
there is no exchange of mass and energy between the system and its
surroundings, Eq. 6 simplifies to:
Closed System
Since
there is no exchange of mass between the system and its surroundings, i.e., dmin
= dmout = 0, Eq. 6 simplifies to:
Steady State System
Noting that:
dmin = dmout = dm and
d(mŜ)sys
= 0
Equation 6 simplifies to:



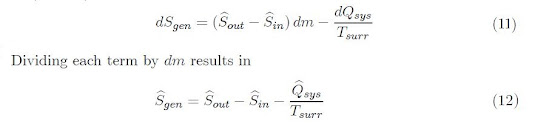




No comments:
Post a Comment