Clausius and Kelvin-Plank statements are the commonly accepted statements of the second law of thermodynamics. These statements are equivalent, and one necessarily implies the other.
Clausius Statement
It is impossible to construct a device operating in a cycle that produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a cooler to a hotter body. Simply put, spontaneous heat transfer from a cooler body to a hotter body is not possible without any external work.
This is illustrated as follows:
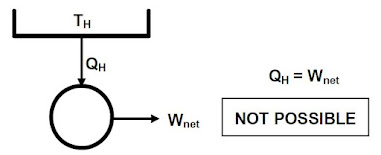
Kelvin-Plank statement
It is impossible to construct a device operating in a cycle that produces no effect other than the extraction of heat from a reservoir and the producing an equal amount of work. This is illustrated as follows:
Example
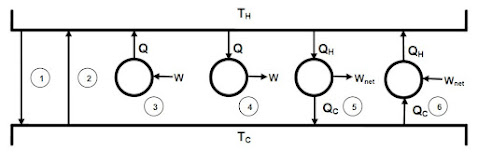
Among the processes shown in below,
identify the ones that are possible:
Solution
- Case 1: Heat flows spontaneously from hot to cold reservoir. From our everyday experience we know that this is possible.
- Case 2: Heat flows spontaneously from cold to hot reservoir. According to the Clausius statement this is impossible.
- Case 3: Work is completely converted to heat. This is possible.
- Case 4: Heat is completely converted into work. This phenomenon violates the Kelvin-Planck statement and hence, it is impossible.
- Case 5: Part of the heat received from a high-temperature reservoir is converted into work while the rest is discarded to a low-temperature reservoir. This represents a typical heat engine and it is possible.
- Case 6: Reverse of Case 5, i.e., work is done on the system, heat is transferred from a low-temperature reservoir to a high-temperature reservoir. Heat pumps (or, refrigerators) operate on this principle hence is possible.





No comments:
Post a Comment